和小弟我一起来探讨Linux中fork与mutex的混合使用
日期:2014-05-16 浏览次数:21076 次
和我一起来探讨Linux中fork与mutex的混合使用
四 代码分析
一 预备知识
本篇代码要用到的Linux函数
1. fork--Linux创建进程的函数
2. fopen--打开文件的函数
3. fgets--读取文件内容的函数
4. fputs--写文件的函数
5 waitpid--等待子进程的函数
6. sleep--进程休眠的函数
7. pthread_mutex_t--线程互斥锁类型
8. pthread_mutex_init--线程互斥锁初始化
9. pthread_mutex_lock--加锁
10. pthread_mutex_unlock--解锁
11. getpid--获取当前进程的id
12. getppid--获取当前进程的父进程的id
二 问题描述
开启子进程去并发读文件内容,然后写入到另一个文件中,父进程不参与文件的读、写。
三 代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
/*
* A instance to use mutex lock
* */
const int MAXSIZE = 1024;
int main() {
FILE *srcfp, *destfp;
int num = 0; // the number of lines from source file
static int over; // whether the read process should be over
char buffer[MAXSIZE];
pid_t pid;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
if((srcfp = fopen("/host/study/C/Linux_Huche/read.c", "r")) == NULL) {
perror("open source file error!\n");
exit(1);
}
if((destfp = fopen("/host/study/C/Linux_Huche/write.c", "w")) == NULL) {
perror("open destination file error!\n");
exit(1);
}
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
while(1) {
if(over) goto End; // to close the files
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) {
puts("now in the child process!\n");
if(fgets(buffer, MAXSIZE, srcfp) == NULL) {
over = 1;
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
sleep(1);
/*
* the critical section
* */
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(over) exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
printf("the getpid() is: %d\n", getpid());
printf("the getppid() is: %d\n", getppid());
printf("num = %d\n", ++num);
puts(buffer);
fputs(buffer, destfp);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
else {
sleep(1);
/*
* to wait for children processes to be over
* */
if(waitpid(pid, NULL, 0) < 0) {
perror("waitpid error!\n");
exit(2);
}
puts("child process is over, now in the parent process!\n");
printf("the getpid() is %d\n", getpid());
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
}
/*
* never not to forget to close the file which is still open
* */
End:fclose(srcfp);
fclose(destfp);
return 0;
}
四 代码分析
1. 主循环是一个死循环,当over = 1时,退出循环;
2. 当创建子进程成功后,子进程首先检测源文件是否读完,如果读完,直接退出。否则,进入临界区向目标文件写数据。
3. 父进程等待子进程运行结束后执行。
4. 子进程中的sleep函数的使用是休眠自己,Linux内核则调度其它子进程执行。
5. 子进程属于并发执行。
6. 最后程序关闭文件后退出。
五 运行结果
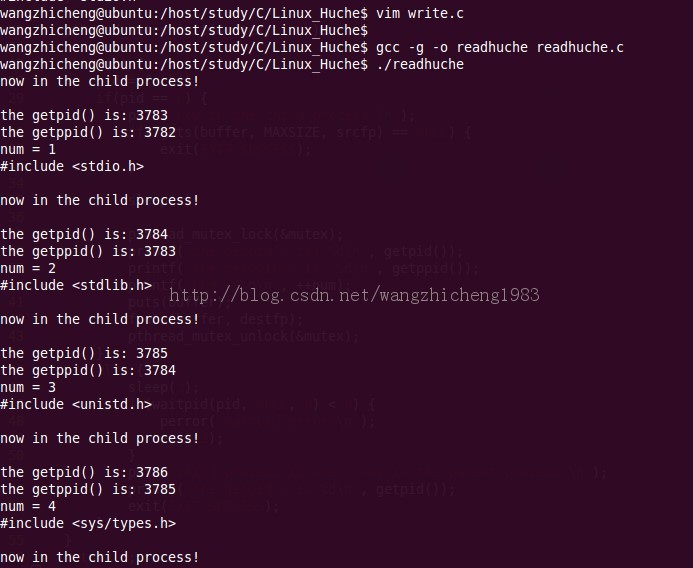
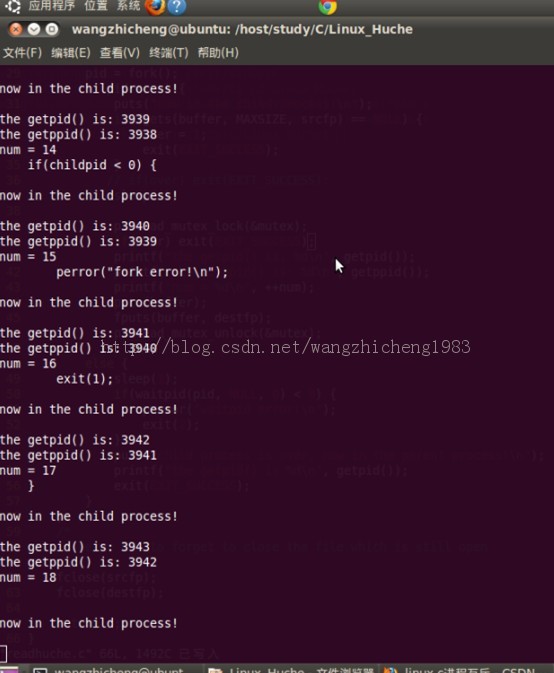
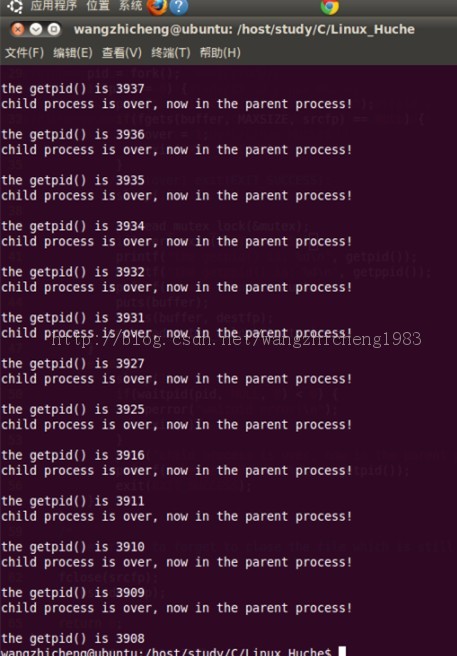
六 运行结果分析
1. 子进程的getppid和父进程的getpid相同;
2. 进程的pid和ppid从小大依次出现,ppid比pid小1;
3. 打开write.c文件,结果如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
/*
* the instance of waitpid
* */
void main() {
pid_t childpid;
int status;
childpid = fork();
if(childpid < 0) {
perror("fork error!\n");
exit(1);
}
else if(childpid == 0) {
puts("in a child process!\n");
printf("the child pid is = %d\n", childpid);
sleep(3);
/*
* the getppid() is the same with getpid() which occurs in parent code section
* */
printf("getpid() is %d\n", getpid());
printf("getppid() is %d\n", getppid());
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else {
/*
* @status: th
免责声明: 本文仅代表作者个人观点,与爱易网无关。其原创性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容、文字的真实性、完整性、及时性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并请自行核实相关内容。
